UX vs UI Design: Key Differences, Roles, and How They Work Together
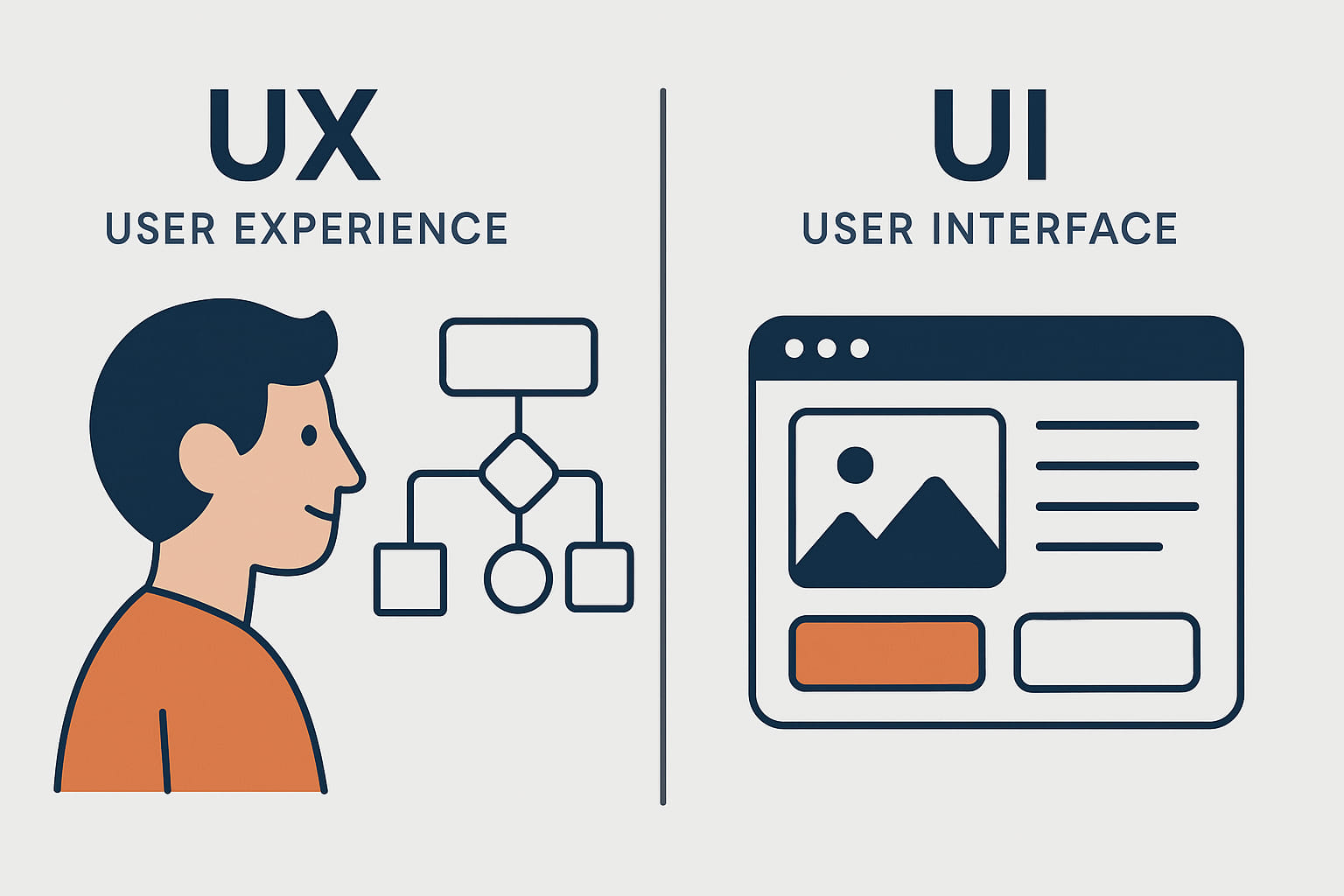
If you’re wondering what the difference between UX design and UI design is, you’re not alone. The terms are often used interchangeably, but in reality, they describe two very different concepts.
UX vs UI in a nutshell
- UX Design (User Experience Design):Focuses on how intuitive, easy, and enjoyable it is to use a product (such as a website, mobile app, or digital platform). It involves researching user needs and creating a logical, seamless structure.
- UI Design (User Interface Design):Focuses on the visual and interactive elements of a product. This includes designing screens, buttons, menus, icons, typography, and interactive states. The goal is to build digital products that are visually engaging, consistent, and easy to use.
Keep reading to learn themain differences between UX and UI, how they complement each other, and what their roles, responsibilities, and even salaries look like.
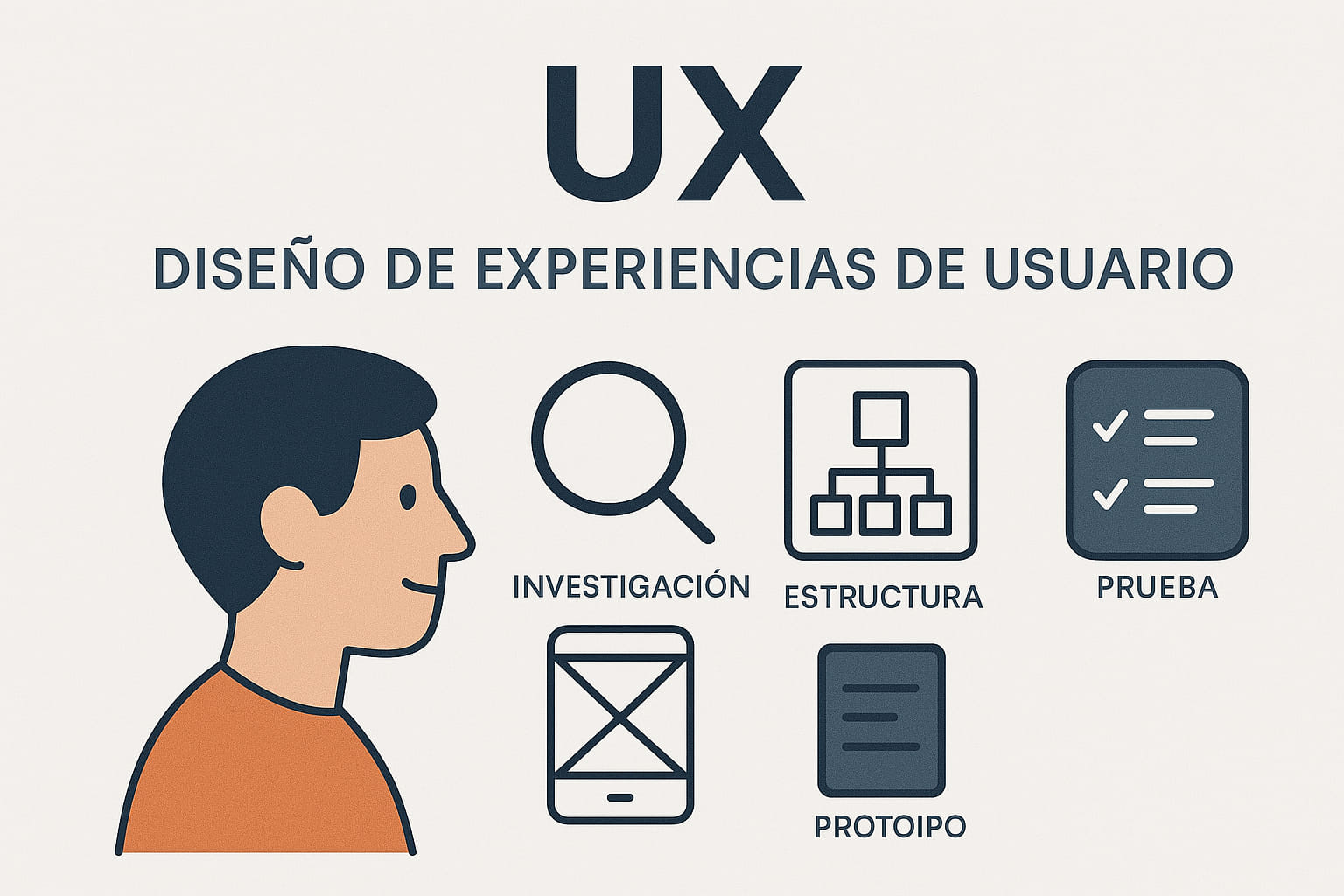
What is UX Design? (User Experience Design)
UX design defines the complete journey of the user when interacting with a product. It answers questions like:
- What user problem does this product solve?
- What features and functions does the user need?
- How should the product be structured to be logical and intuitive?
- How should information and content be organized?
- How does the userfeelwhile using it?
Think of UX design as thefoundationof a digital product — the blueprint that everything else is built on.
What does a UX designer do?
Typical UX designer responsibilities include:
- Research & strategy:competitor analysis, user research, customer journey mapping, content strategy.
- Wireframing & prototyping:wireframes, low- and high-fidelity prototypes, user testing, iteration.
- Collaboration:working closely with UI designers and developers.
- Analysis & optimization:setting goals, measuring results, improving user flows.
In short,UX designersconnect business goals with user needs by continuously testing and improving digital products.
What is UI Design? (User Interface Design)
Unlike UX, which focuses on structure and usability,UI designis all about how the product looks and feels on screen.
AUI designertakes the UX framework and brings it to life visually with typography, colors, spacing, images, buttons, icons, animations, and responsive layouts.
Key questions UI designers ask:
- What elements should appear on each screen or page?
- Where should they be placed for maximum clarity?
- What happens when a user clicks or taps a button?
- How do different screens connect and transition?
- How can the interface be visually appealing and consistent with brand identity?
What does a UI designer do?
TypicalUI designer tasksinclude:
- Visual design & branding:typography, color palettes, iconography, layout design, style guides.
- Interactivity:microinteractions, animations, hover effects, transitions.
- Responsive design:ensuring usability across devices and screen sizes.
- Collaboration:working with UX designers and developers to bring interfaces to life.
UI is100% digitaland directly shapes how users experience a product on screen.
Understanding the Key Differences Between UX and UI

UX vs UI: Key Differences
Here’s a quick UX vs UI comparison:
- UX design= the complete user journey, structure, logic, and usability.
- UI design= the visual and interactive layer that makes the product attractive and functional.
- UX is broader(it can apply to digital and non-digital experiences, like a car dashboard or a store layout).
- UI is specific to digital products(websites, apps, software).
- UX usually comes first→ UI builds on it to create the final interface.
In other words:
👉 UX is about problem-solving and user satisfaction.
👉 UI is about presentation and interaction.
"Something that looks great but is hard to use is an example of good UI and poor UX. Something highly functional but unattractive is good UX and poor UI."
Helga Moreno
Why UX and UI Work Best Together
You might be asking: Is UX more important than UI? The truth is:both are essential.
- A product with a great UI but poor UX might look amazing but be frustrating to use.
- A product with a strong UX but weak UI might be functional but unattractive and hard to trust.
As designer Helga Moreno once said:
“Something that looks great but is hard to use is an example of good UI and poor UX. Something highly functional but unattractive is good UX and poor UI.”
The most successful digital products — whether websites, apps, or SaaS platforms — combine strong UX with strong UI.
Final Thoughts: UX vs UI in Digital Design
- UX (User Experience Design):focuses on research, structure, usability, and problem-solving.
- UI (User Interface Design):focuses on visuals, interactivity, and brand consistency.
- Both are crucial for creatingdigital products that users love.
Whether you’re thinking of becoming aUX designeror aUI designer, understanding both fields will make you a stronger professional — and will help you build digital experiences that are not only beautiful but also effective and user-friendly.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about UX and UI
1. What is the main difference between UX and UI?
UX (User Experience) focuses on the overall journey and usability of a product, while UI (User Interface) focuses on the visual design and interactive elements. In short: UX is about how itworksand UI is about how itlooks.
2. Do I need both UX and UI design for a website or app?
Yes. A great UI without UX can look attractive but be hard to use. A great UX without UI can be functional but unattractive. For a successful digital product, you need both.
3. Which comes first: UX or UI design?
UX design usually comes first, defining the structure, flow, and functionality. UI design follows, bringing the visuals, branding, and interactivity to life.
4. Can UX exist without UI?
Yes — UX is broader and can be applied to non-digital experiences (like customer service or physical products). UI, however, only exists in digital environments.
5. Is UX more important than UI?
Neither is more important; they serve different purposes. UX ensures usability and satisfaction, while UI ensures aesthetics and engagement. The best digital products combine both.
6. What skills does a UX designer need?
UX designers need skills in user research, wireframing, prototyping, information architecture, usability testing, and data analysis.
7. What skills does a UI designer need?
UI designers need skills in visual design, typography, color theory, responsive design, prototyping tools, and interaction/animation design.
8. Do UX designers need to code?
Not always. Some companies require basic front-end knowledge (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), but the role is primarily design and research focused.
9. Do UI designers need to code?
Traditionally, no. But today, many UI designers also have front-end skills (sometimes called UI developers) to implement their designs.
10. What are the salaries of UX and UI designers?
Salaries vary by country, experience, and industry. Generally, both roles are in high demand, with UX designers often earning slightly more due to their involvement in strategy and research.
